Ancient Egypt, one of the most captivating civilizations in history, thrived for over 3,000 years along the banks of the Nile River. Its remarkable achievements in architecture, art, religion, and governance continue to intrigue and inspire us today. In this article, we will delve into the captivating history of ancient Egypt, tracing its roots from the prehistoric era to its ultimate decline. Through a chronological exploration, we will uncover the remarkable pharaohs, monumental structures, cultural practices, and religious beliefs that shaped this extraordinary civilization.
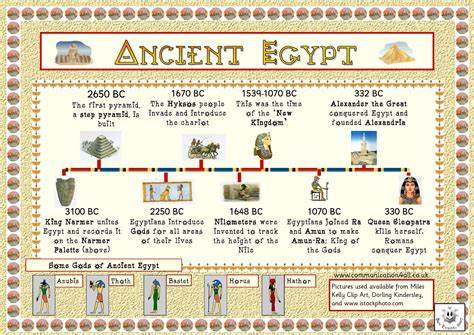
Ancient Egyptian civilization emerged around 3100 BCE, but the foundations were laid much earlier during the prehistoric era. The Nile Valley provided a fertile environment for early settlements, leading to the development of agriculture and the formation of organized communities. The Archaic Period witnessed the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under King Narmer, creating the first dynasty and initiating the era of pharaohs.
The Old Kingdom, spanning from 2686 to 2181 BCE, was characterized by the construction of massive pyramids, including the iconic Great Pyramid of Giza. Pharaohs, considered divine rulers, centralized power and established a theocratic society. Hieroglyphic writing, the earliest known form of Egyptian writing, emerged during this period, reflecting the importance of record-keeping and administration.
The Middle Kingdom (2055-1650 BCE) marked a period of political and cultural resurgence after a time of decentralization and foreign invasions. Pharaohs focused on public welfare and irrigation projects, aiming to improve the lives of their subjects. Literature, such as “The Tale of Sinuhe,” flourished during this era, depicting both fictional and historical narratives.
The New Kingdom (1550-1069 BCE) witnessed the zenith of ancient Egyptian power and influence. Pharaohs like Hatshepsut, Thutmose III, and Ramses II expanded Egypt’s borders through military conquests and established diplomatic relations with neighbouring civilizations. The reign of Akhenaten introduced a radical shift in religious practices with the worship of the Aten, the sun disc. Tutankhamun, one of the most famous pharaohs, restored the traditional religious beliefs and sparked immense interest through the discovery of his intact tomb in the Valley of the Kings.
The Late Period (1069-332 BCE) was marked by a series of invasions and foreign dominations. The Assyrians, Persians, and Greeks successively conquered Egypt, each leaving their imprint on the culture and administration of the land. The Ptolemaic Dynasty, descended from one of Alexander the Great’s generals, ruled Egypt for nearly three centuries and witnessed the famous queen Cleopatra’s reign.
The decline of ancient Egypt came with the Roman conquest in 30 BCE. Despite its political downfall, Egypt’s cultural and architectural legacy continued to captivate the world. The decipherment of hieroglyphics in the 19th century allowed for a deeper understanding of the civilization. Today, visitors flock to marvel at the Great Pyramids, the Sphinx, and the temples of Luxor and Karnak, immortalizing the architectural prowess and spiritual beliefs of ancient Egypt.
The history of ancient Egypt is a testament to the remarkable achievements of a civilization that thrived for thousands of years.



Comment (0)